| perturbed state wherein the system, even when not disturbed, will not remain in a steady state, or cannot spontaneously return to a steady state after being subjected to a disturbance of prescribed magnitude 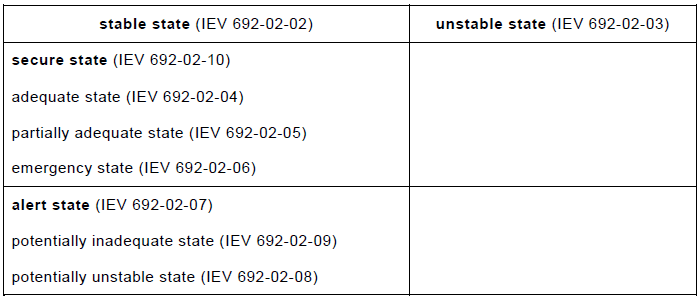
Figure 2 – Electric power system states 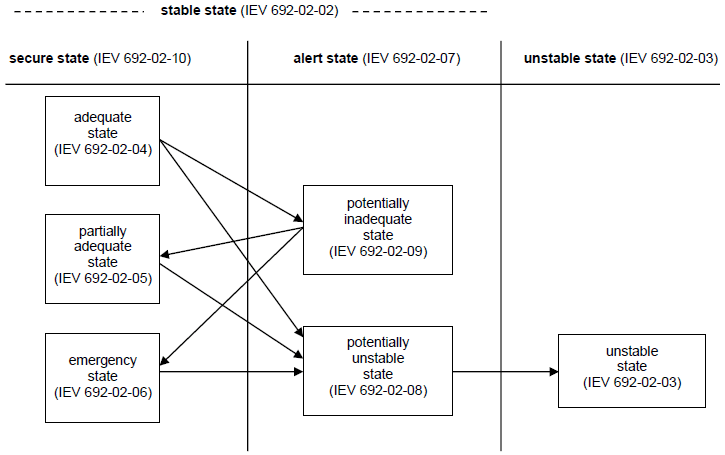
NOTE The arrows indicate the most important state transitions caused by credible events. Recovery transitions, in opposite directions, are effected by operator intervention. Figure 3 – Examples of transitions within electric power system states Note 1 to entry: In an unstable state, the electric power system is experiencing cascade tripping, voltage instability or other instability likely to result in system collapse. Note 2 to entry: This entry was numbered 191-22-02 in IEC 60050-191:1990.
|