| small localized wave, represented by a function having a zero mean value and a practically finite duration Note 1 to entry: From a mother wavelet , daughter wavelets are obtained through shifting and scaling (expansion or compression): , where a is a scale parameter and b a position parameter. Note 2 to entry: Examples (see Figures 3 and 4): - Haar wavelet: for −1/2 < t < 0, for 0 < t < 1/2, outside;
- Morlet wavelet: (example of exponential damping; Figure 4 gives the real part).
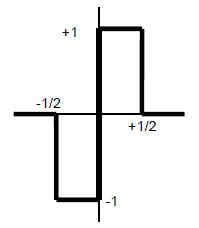
Figure 3 – Haar wavelet Figure 3 – Ondelette de Haar 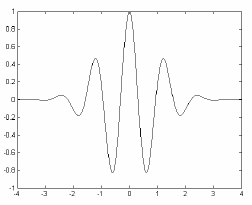
Figure 4 – Morlet wavelet Figure 4 – Ondelette de Morlet
|