| angle subtended at the point of incidence by a given ray in the viewing direction and the specular direction defined by the incident ray and the surface normal Note 1 to entry: The incident and viewing rays, the surface normal and the specular direction all lie in a common plane. Note 2 to entry: The aspecular angle is calculated as the difference between the viewing direction and the specular direction and is understood to be positive when it lies between the specular direction and the incident (illuminating) ray (see the figure below). X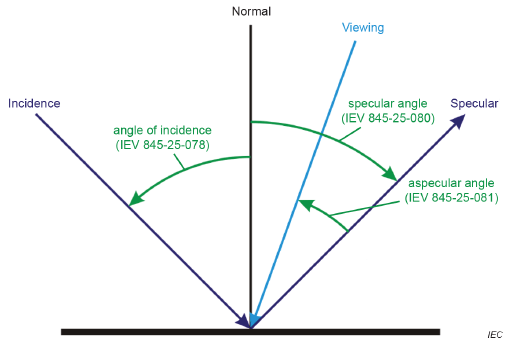 Note 3 to entry: The aspecular angle is measured in radian (rad) or degree (°).
|