| distribution assigning to any function f(x), continuous for , the value f(0) Note 1 to entry: The Dirac function can be considered as the limit of a function, equal to zero outside a small interval containing the origin, and the integral of which remains equal to unity when this interval tends to zero. See Figure 1, where instead of a triangle any other shape with area 1 is possible, too. Note 2 to entry: The Dirac function is the derivative of the unit step function considered as a distribution. Note 3 to entry: The Dirac function can be defined for any value x0 of the variable x. The usual notation is: 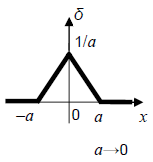
Figure 1 – Dirac function
|